I. Bajšanski, V. Stojaković, M. Jovanović, 2016. Computers, Environment and Urban Systems, Vol. 16. pp.59-67
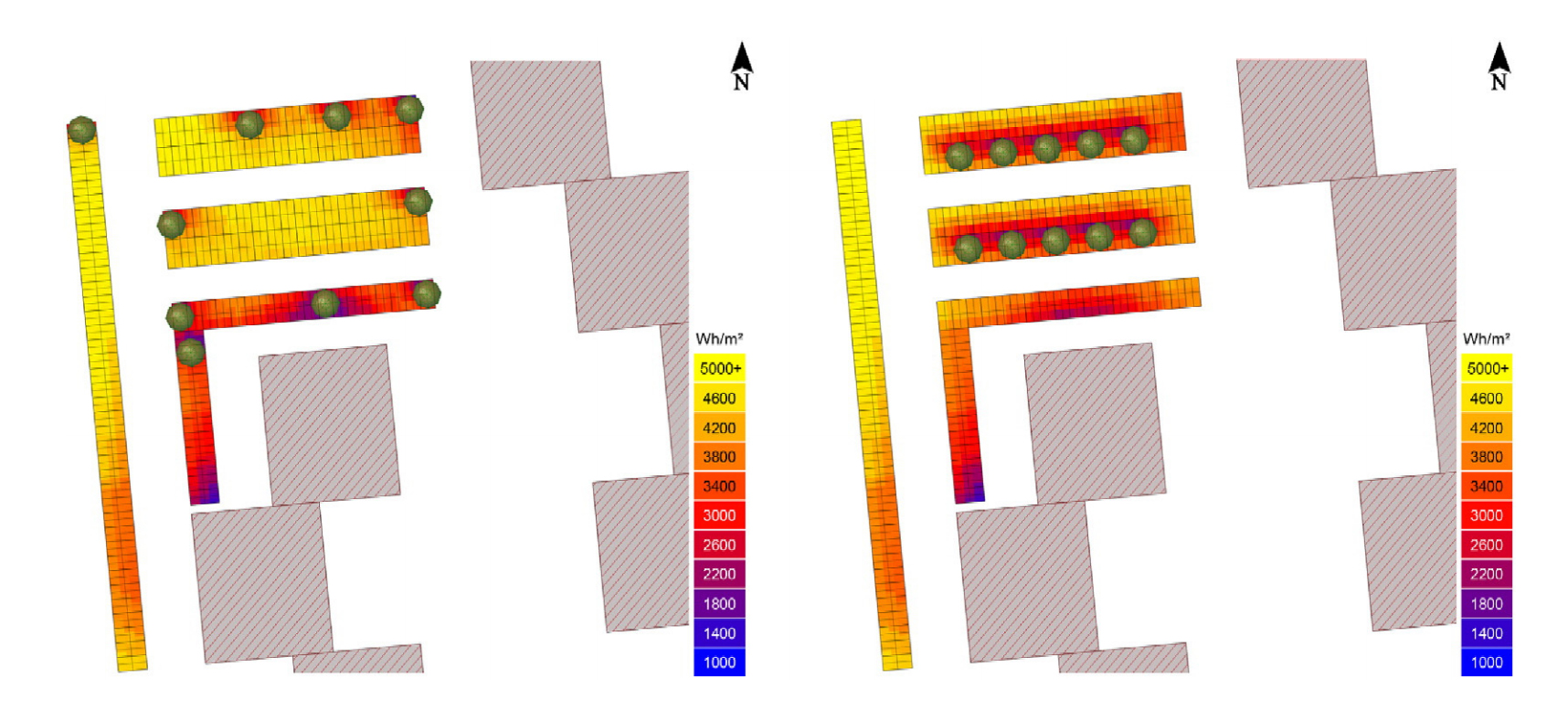
Abstract: Urban land used for parking lots can contribute to the effect of overheating, whereas vegetation, especially high growth vegetation (trees), can mitigate this effect. Accordingly, in this paper we propose an algorithm, the inputs to which consist of predetermined parameters of a parking lot’s geometry, trees and surrounding buildings, where the shadows help to mitigate the heat. The algorithm optimizes tree locations, aiming to provide maximum overshadowing of the parking lots, while leaving the useable parking area and the parking lot shape intact. The paper focuses on parameterization of elements that are important for this analysis process as well as combinatory calculations. These combinatory calculations are based on solar simulations, which are carried out, and take into account climate and geographical data. The algorithm is applied to several cases, depicting real world examples, as well as those based on design and greening instruction manuals. The results indicate that the tree locations estimated by the algorithm increase parking lot overshadowing, indicating that the algorithm efficiently decreases the negative influence of urban overheating.
Online version of article: Effect of tree location on mitigating parking lot insolation