Workshops, Fondazione Bruno Kesler, Trento Italy & Digital Design Center, FTN, University of Novi Sad, 26-28 March 2014.
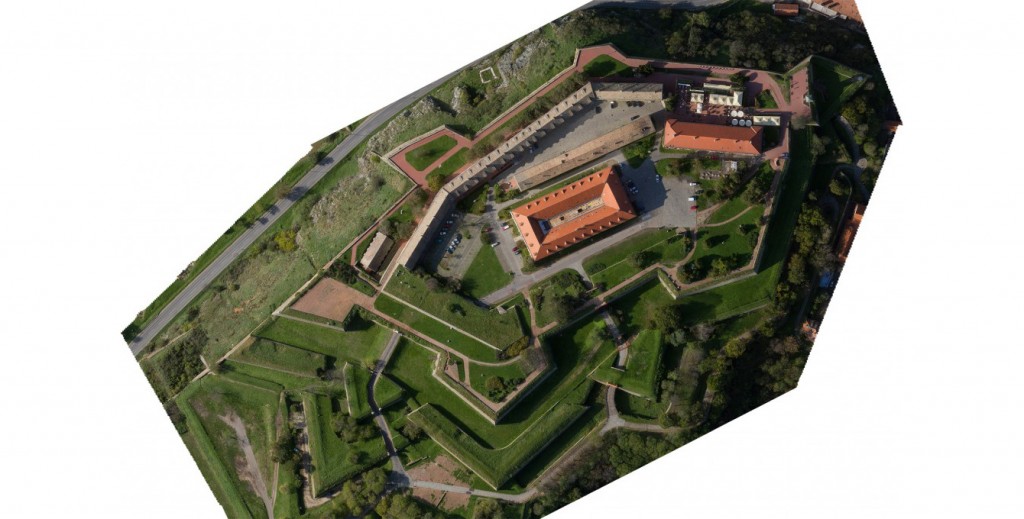
The workshop was held in Novi Sad, under the leadership of FBK, as part of the project GisNS. It focuses on 3D surveying and modeling, with particular attention to the image-based and photogrammetric approach. The workshop consisted of some theoretical lectures (principle of surveying, photogrammetry and laser scanning with examples in the field of Cultural Heritage, city mapping and planning, landscape monitoring, energy demand assessment, etc.) and practical demonstrations with image acquisition on site and data processing in the lab. Result is 3D HighRes model of Petrovaradin Fortress. The workshop was attended by 25 participants, with technical and humanistic background, coming from academia, private companies and cultural institution.



The workshops are organized within the activities of the project “GisNS – Development of Online Geodata Portal of Cultural Heritage in Novi Sad” funded by CEI-KEP (http://www.cei.int/KEP). The GisNS is an interdisciplinary project which aims to solve the problem of missing digitized and well organized 3D Cultural Heritage assets within the geodata portal of Novi Sad (Serbia). The project partners are:
- 3D Optical Metrology (3DOM) unit – Bruno Kessler Foundation (FBK), Trento, Italy
- Faculty of Technical Sciences – Department of Architecture, University of Novi Sad, Serbia
- Public Enterprise for City Construction and Development, Novi Sad, Serbia
- Institute for the Protection of Cultural Monuments of Novi Sad, Serbia
Workshop on Indoor 3D Surveying and Modeling and Presentation of GISNS Project Results
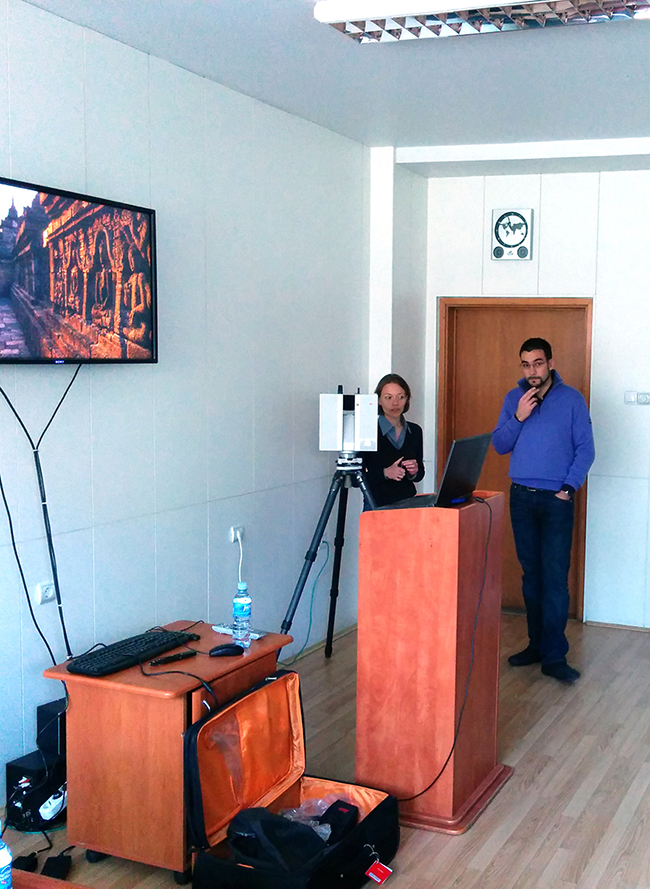
Workshop for knowledge and technology transfer: on 22-23 January 2015, as a part of the GisNS project.
The workshop was held in Novi Sad, under the leadership of Fabio Remondino from FBK, Italy. The focus was on indoor 3D surveying and modeling of cultural heritage, with particular attention to the image-based and photogrammetric approach. The workshop consisted of two theoretical lectures and practical demonstrations with image acquisition on site, in the Museum of Vojvodina, and data processing in the lab at the Faculty of technical sciences. The workshop was attended by participants with technical and humanistic background, coming from academia, private companies and cultural institution.
Petrovaradin Fortress Surveying Using UAVs
Workshop for knowledge and technology transfer: on 27-28 October 2014, as a part of the GisNS project.
In a two day workshop, the upper part of Petrovaradin fortress was surveyed using multirotor-like UAV platform (drone).
The workshop was held in Novi Sad, under the leadership of FBK. It was focused on 3D surveying and modeling, with particular attention to the image-based and photogrammetric approach, using specific UAV platform.