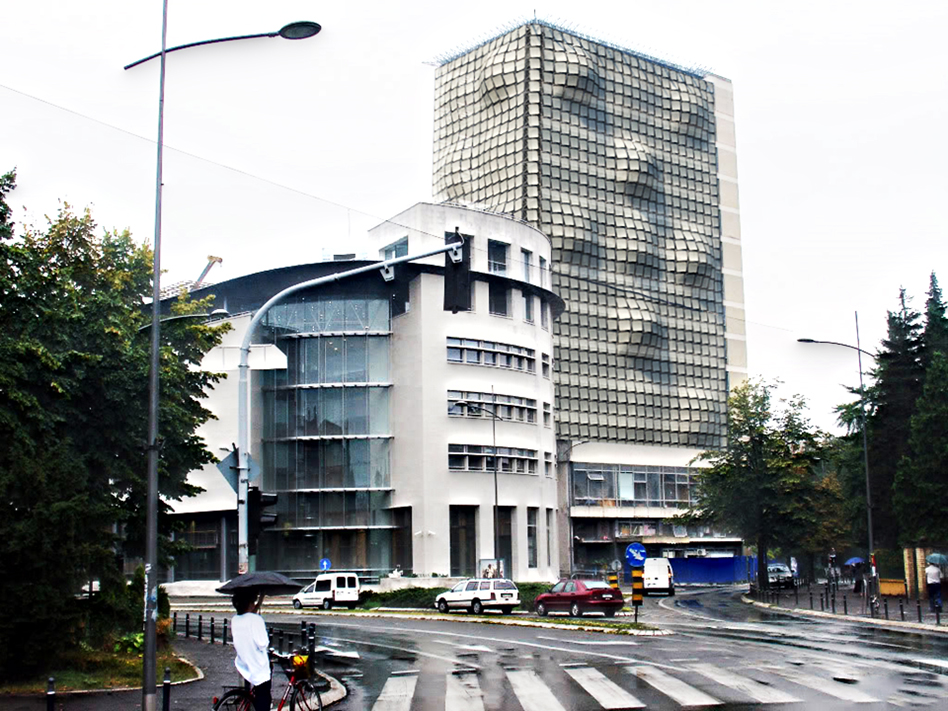
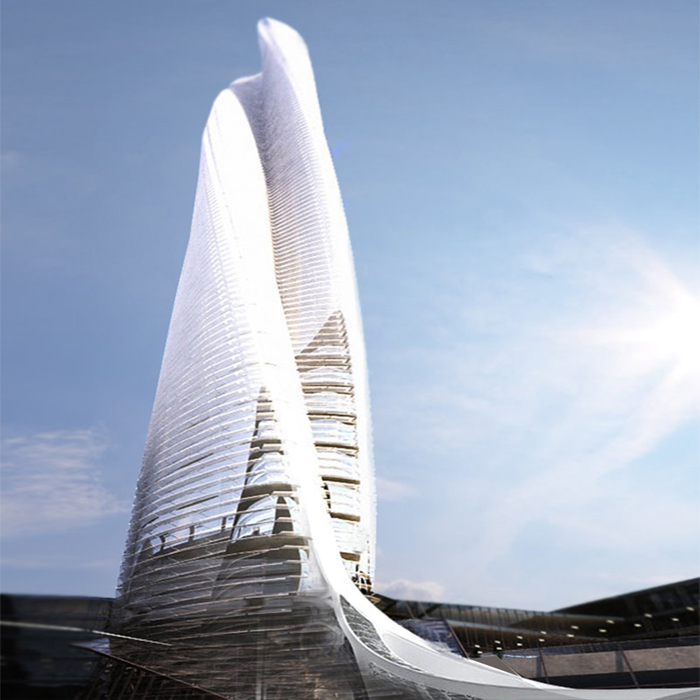
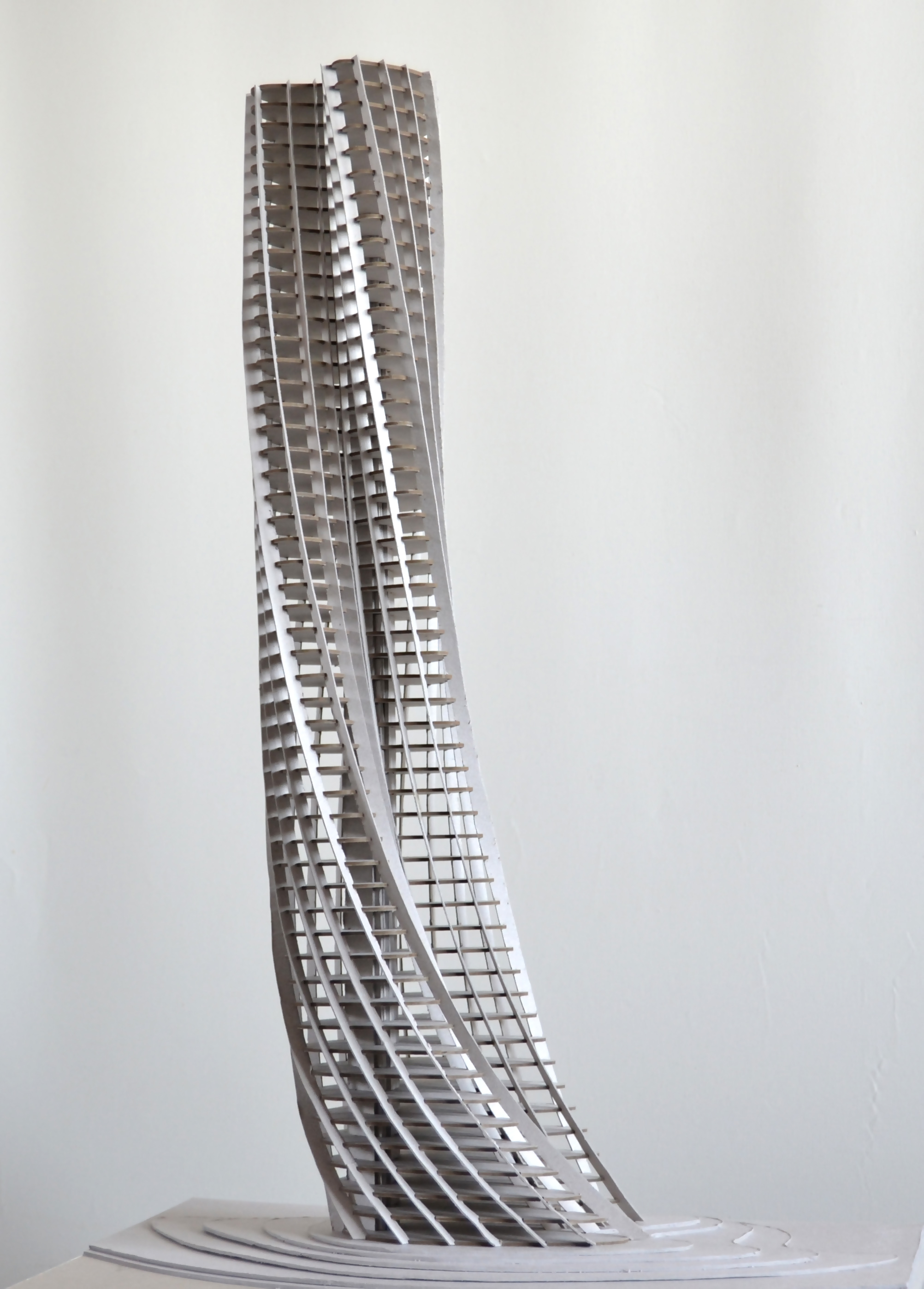
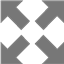
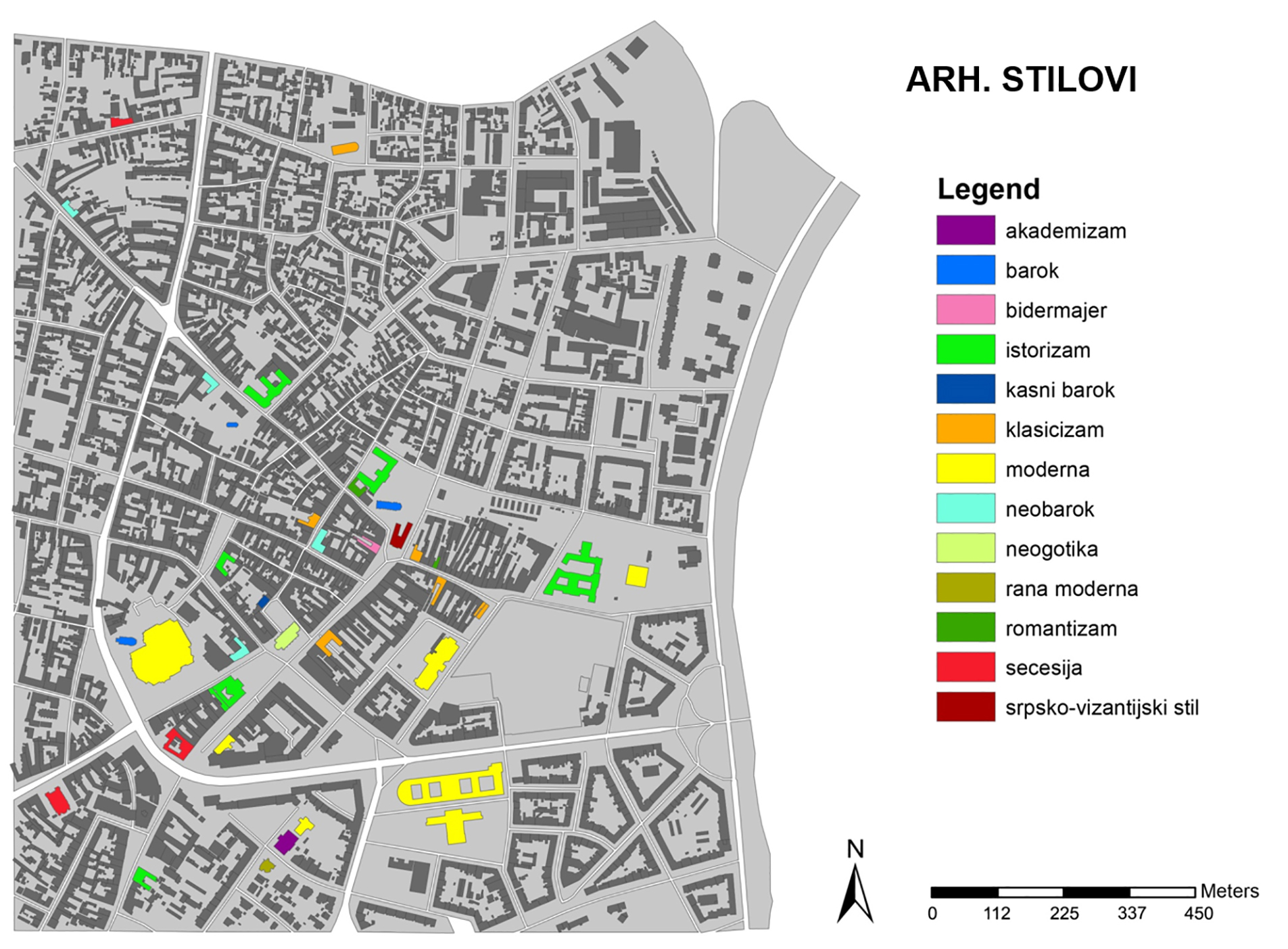
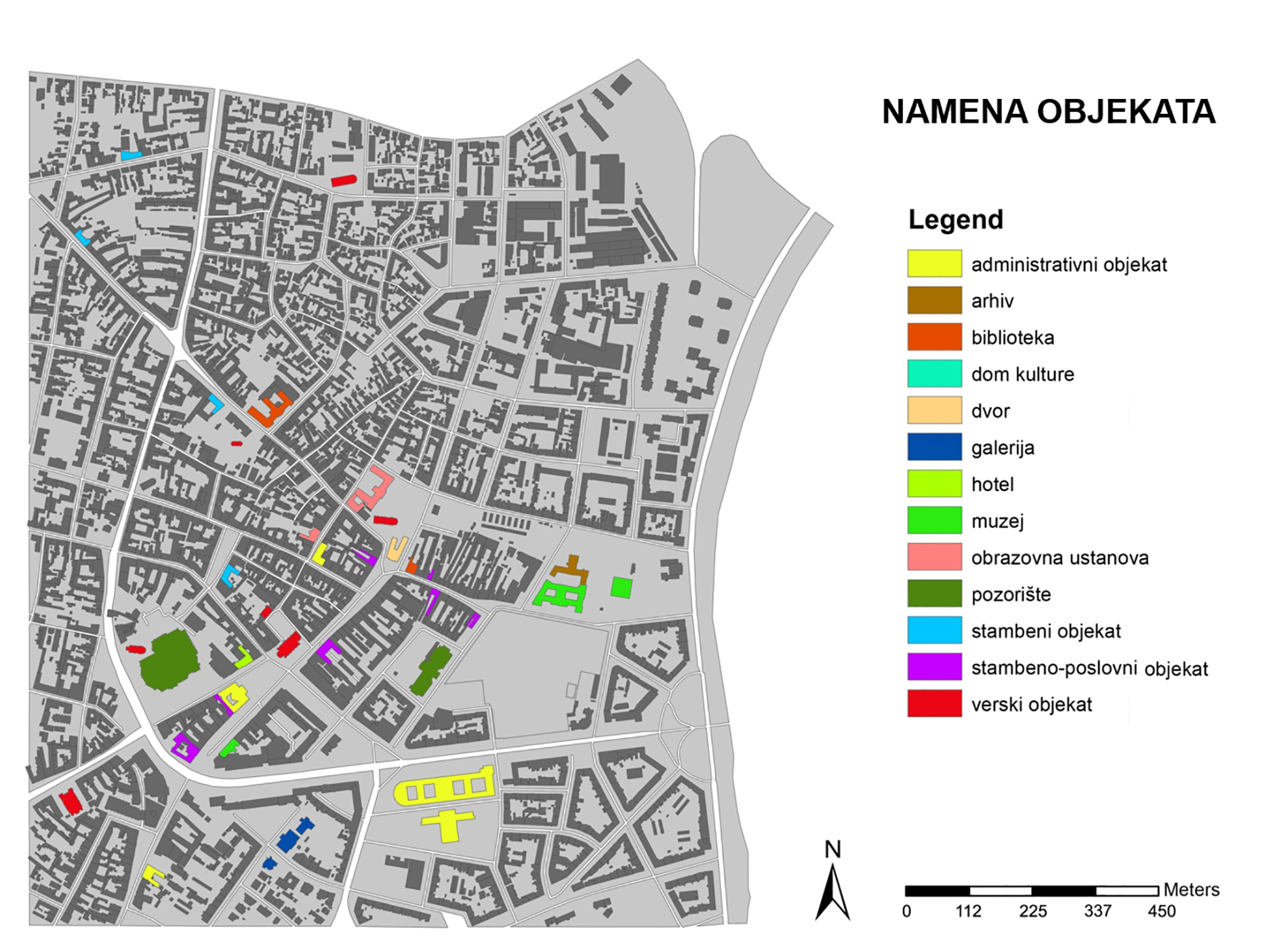
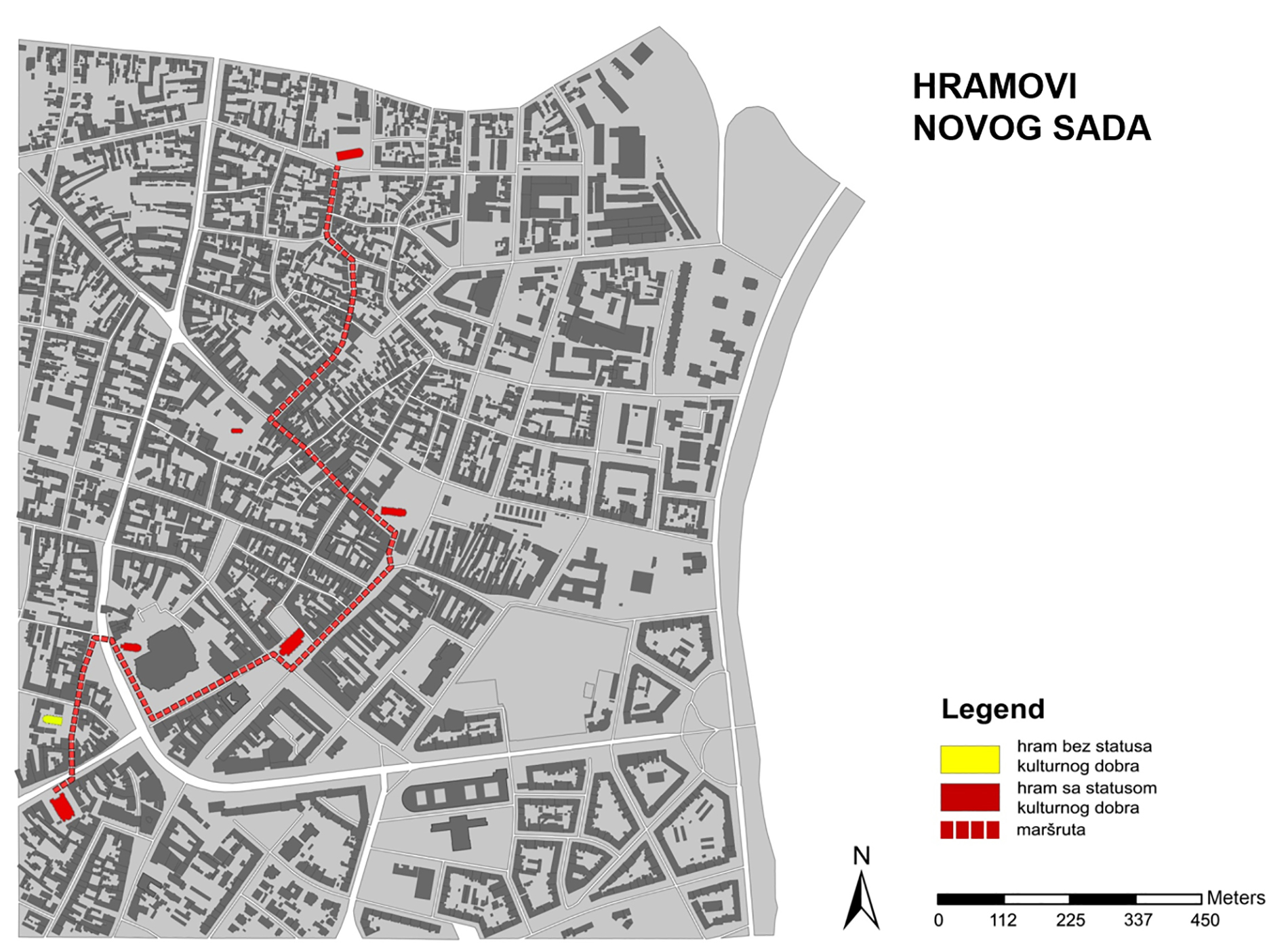
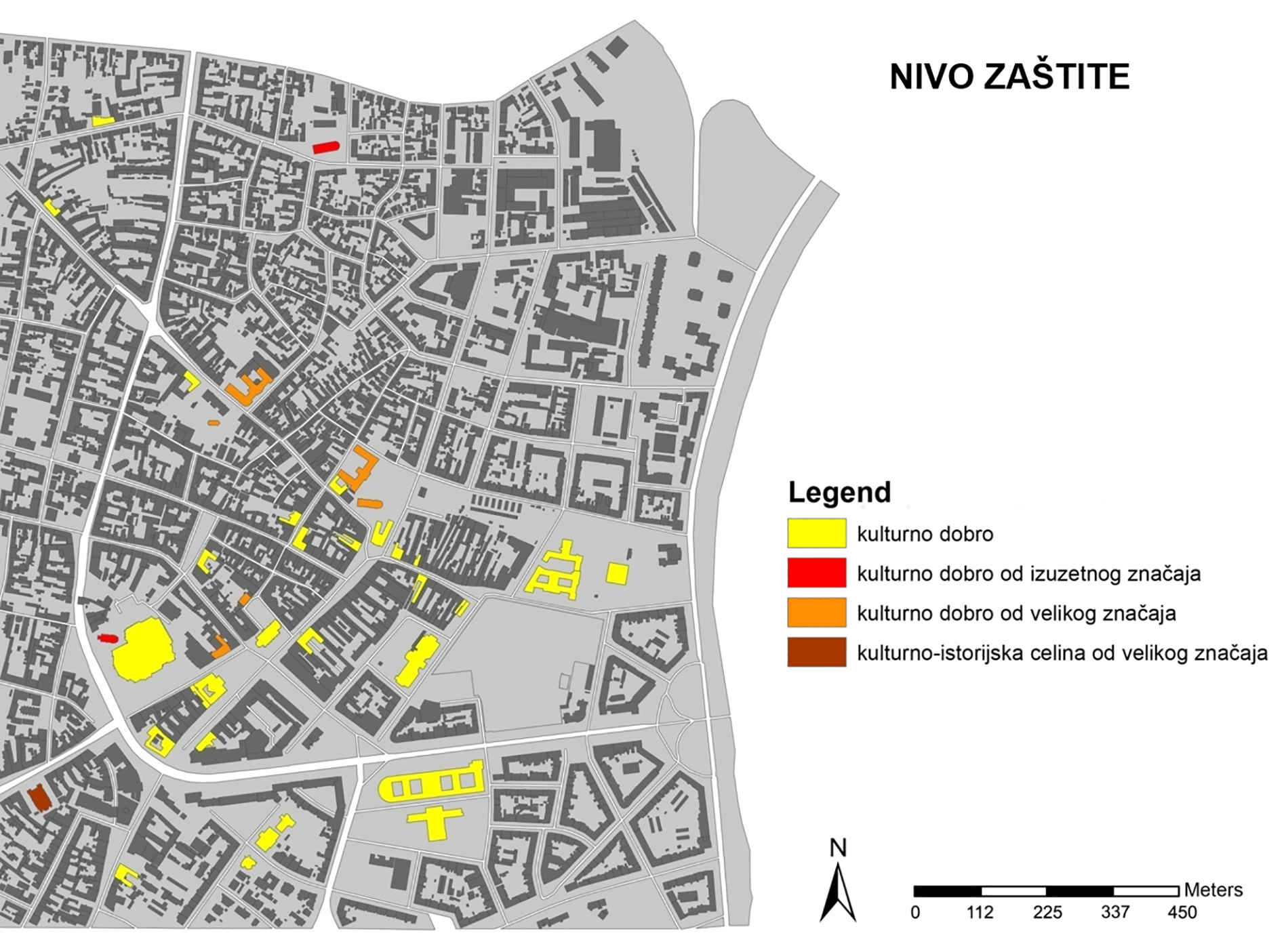
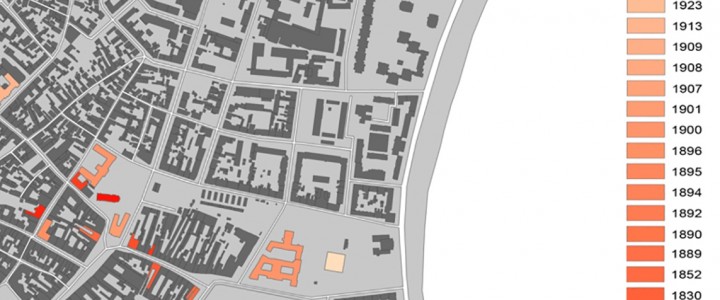
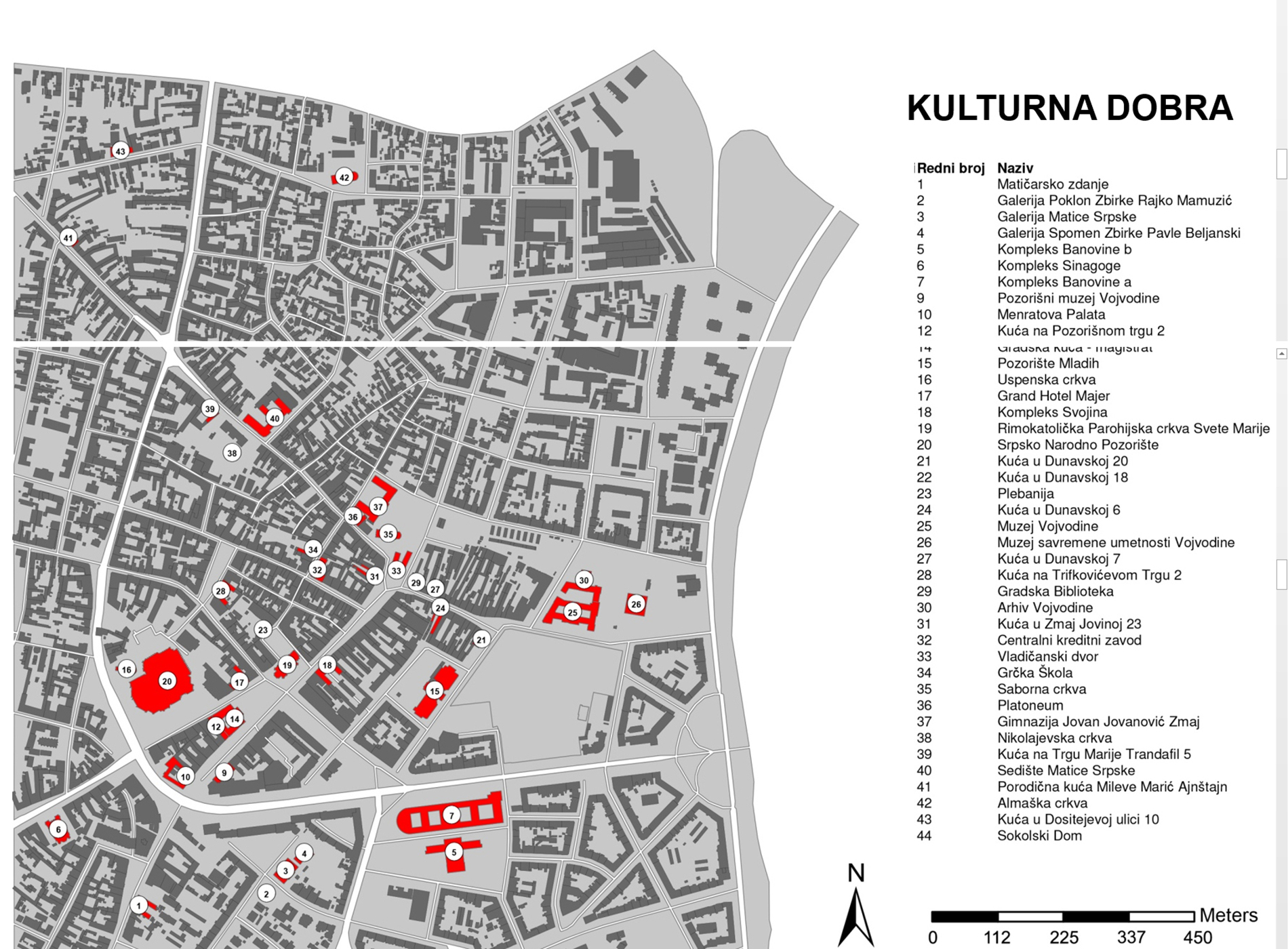
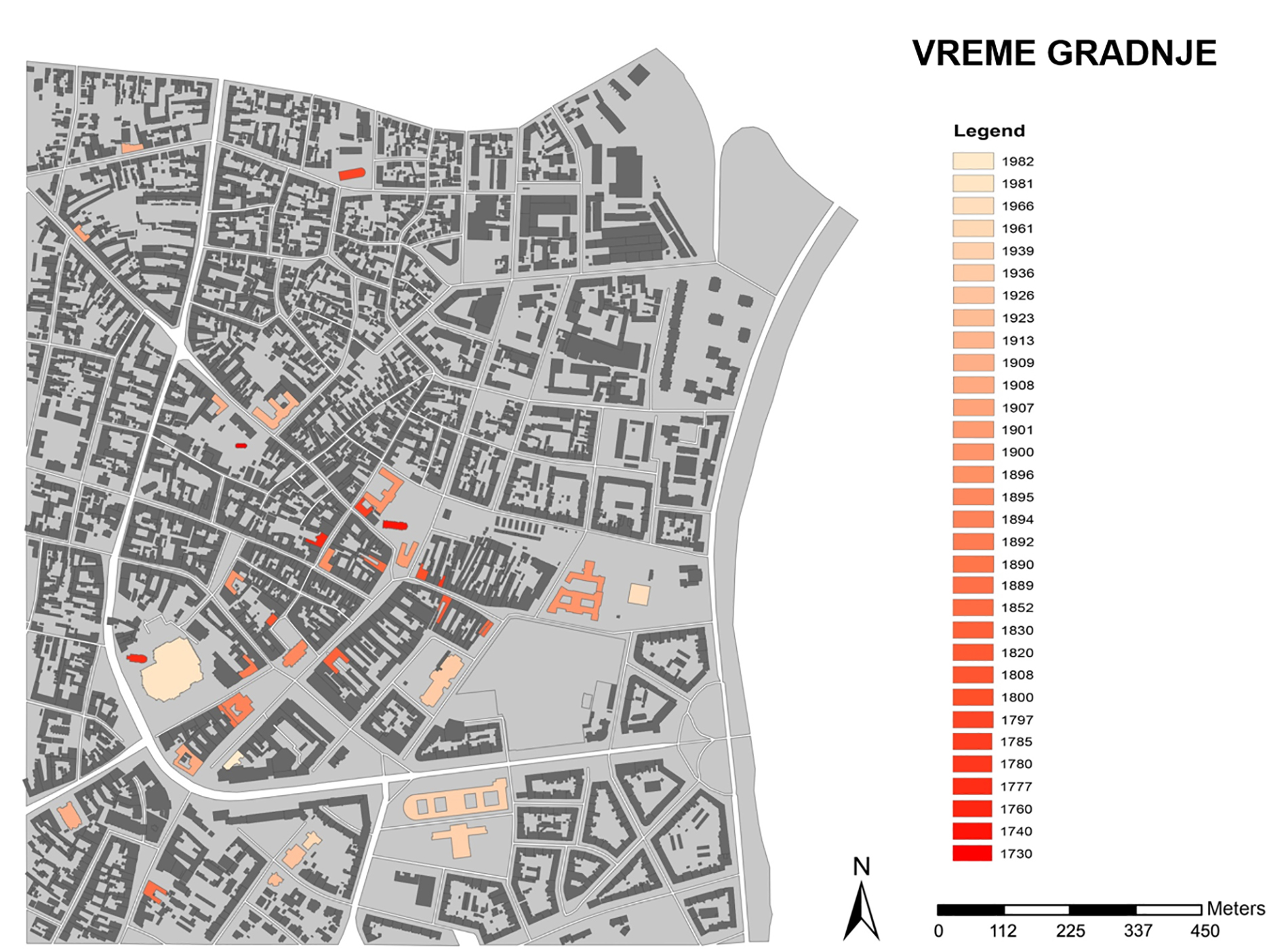
Within this project task, a GIS database of cultural objects in Novi Sad was created. Based on the data from the site of the Institute for the Protection of Cultural Monuments of Novi Sad, most of the objects of the narrow city core are selected, which represent the immovable cultural heritage of Novi Sad, together with its attributes (address, floor, style, year of construction, designer, type of cultural property). Based on the data entered, GIS analysis in ArcGIS software are presented which shows the position of objects in the city tissue in relation to one of their characteristics (year of construction, style, etc.). The significance of this analysis is that the obtained results can be applied in further protection or creating further tourist offer-e.g. creating walking routes for touring objects in a city of a certain style or age.
Student: Mladen Papović



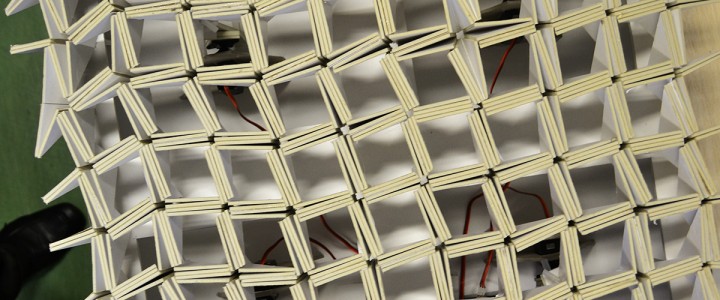
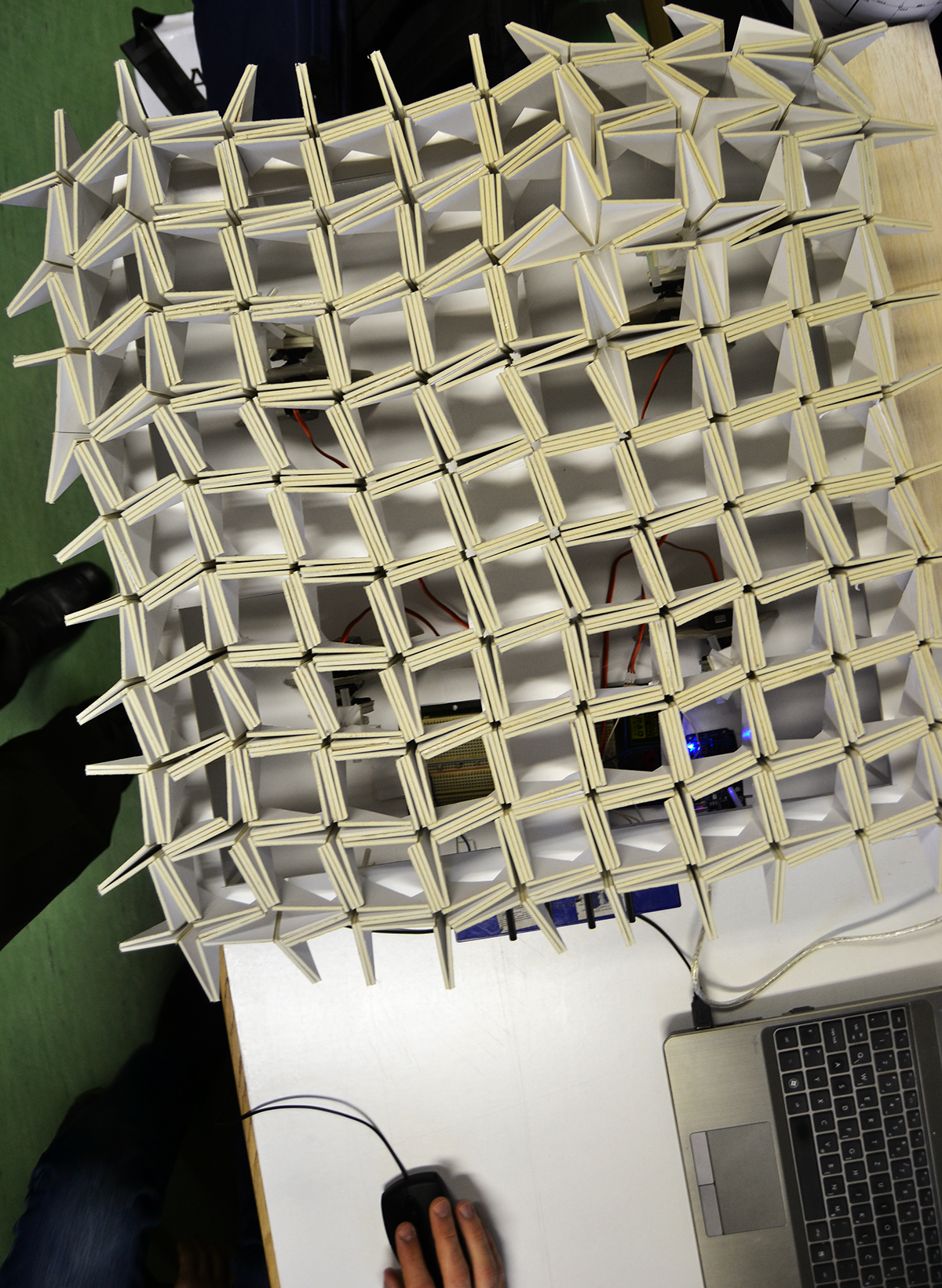
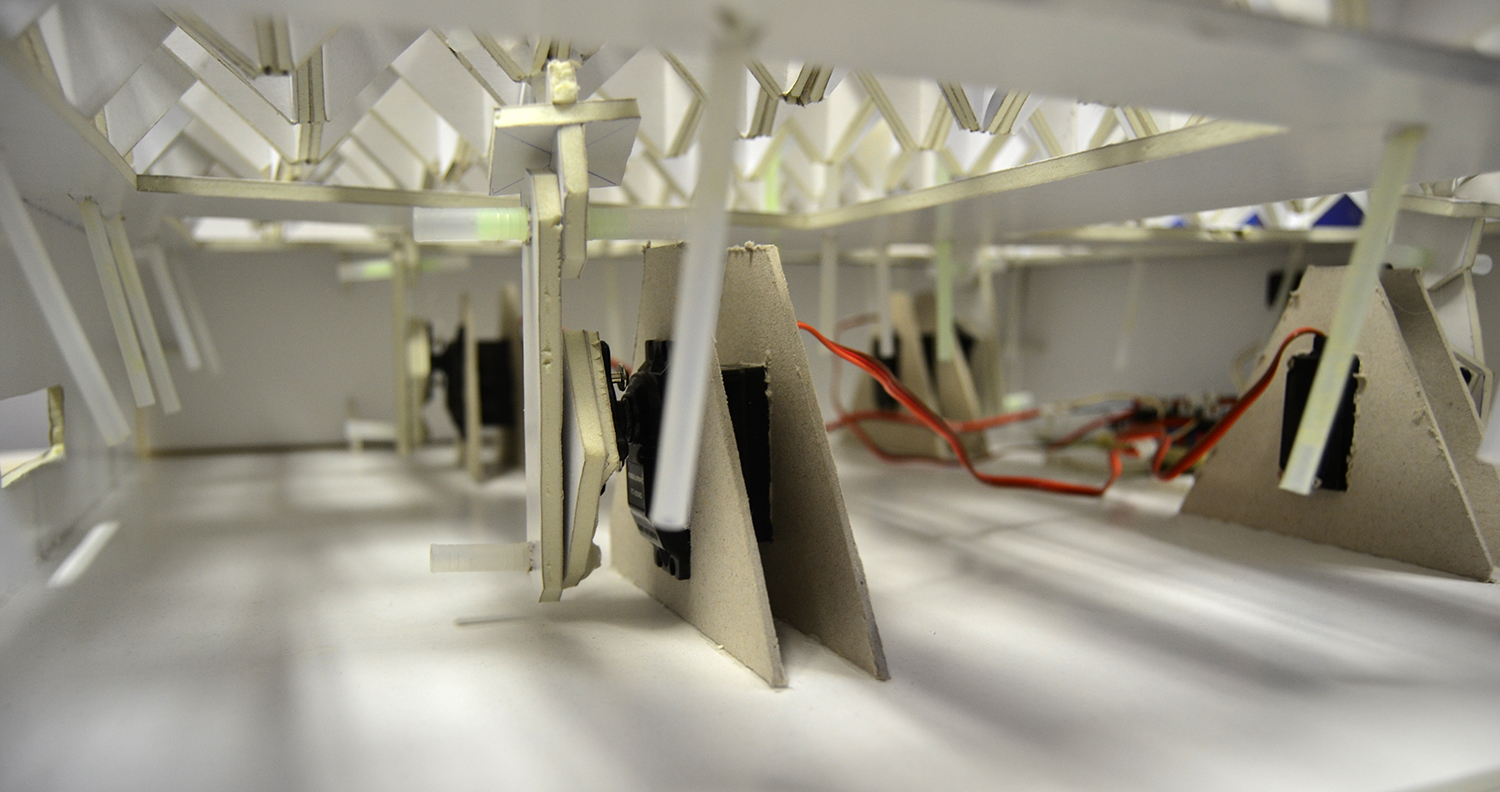
![FOLDED[skins] – Design to Fabrication FOLDED[skins] – Design to Fabrication](https://www.arhns.uns.ac.rs/digital/wp-content/uploads/2015/08/1-e1467412166807-720x300.jpg)